The recent trend of threat actors using information stealer malware, designed to gather and exfiltrate confidential data, shows no sign of slowing. With new or updated info-stealer strains appearing in the wild on a regular basis, it came as no surprise to see a surge in yet another prolific variant in late 2022, CryptBot.
What is CryptBot?
CryptBot is a Windows-based trojan malware that was first discovered in the wild in December 2019. It belongs to the prolific category of information stealers whose primary objective, as the name suggests, is to gather information from infected devices and send it to the threat actor.
ZeuS was reportedly the first info-stealer to be discovered, back in 2006. After its code was leaked, many other variants came to light and have been gaining popularity amongst cyber criminals [1] [2] [3]. Indeed, Inside the SOC has discussed multiple infections across its customer base associated with several types of stealers in the past months [4] [5] [6] [7].
The Darktrace Threat Research team investigated CryptBot infections on the digital environments of more than 40 different Darktrace customers between October 2022 and January 2023. Darktrace DETECT™ and its anomaly-based approach to threat detection allowed it to successfully identify the unusual activity surrounding these info-stealer infections on customer networks. Meanwhile, Darktrace RESPOND™, when enabled in autonomous response mode, was able to quickly intervene and prevent the exfiltration of sensitive company data.
Why is info-stealer malware popular?
It comes as no surprise that info-stealers have “become one of the most discussed malware types on the cybercriminal underground in 2022”, according to Accenture’s Cyber Threat Intelligence team [10]. This is likely in part due to the fact that:
More sensitive data on devices
Due to the digitization of many aspects of our lives, such as banking and social interactions, a trend accelerated by the COVID-19 pandemic.
Cost effective
Info-stealers provide a great return on investment (ROI) for threat actors looking to exfiltrate data without having to do the traditional internal reconnaissance and data transfer associated with data theft. Info-stealers are usually cheap to purchase and are available through Malware-as-a-Service (MaaS) offerings, allowing less technical and resourceful threat actors in on the stealing action. This makes them a prevalent threat in the malware landscape.
How does CryptBot work?
The techniques employed by info-stealers to gather and exfiltrate data as well as the type of data targeted vary from malware to malware, but the data targeted typically includes login credentials for a variety of applications, financial information, cookies and global information about the infected computer [8]. Given its variety and sensitivity, threat actors can leverage the stolen data in several ways to make a profit. In the case of CryptBot, the data obtained is sold on forums or underground data marketplaces and can be later employed in higher profile attacks [9]. For example, stolen login information has previously been leveraged in credential-based attacks, which can successfully bypass authentication-based security measures, including multi-factor authentication (MFA).
CryptBot functionalities
Like many information stealers, CryptBot is designed to steal a variety of sensitive personal and financial information such as browser credentials, cookies and history information and social media accounts login information, as well as cryptocurrency wallets and stored credit card information [11]. General information (e.g., OS, installed applications) about the infected computer is also retrieved. Browsers targeted by CryptBot include Chrome, Firefox, and Edge. In early 2022, CryptBot’s code was revamped in order to streamline its data extraction capabilities and improve its overall efficiency, an update that coincided with a rise in the number of infections [11] [12].
Some of CryptBot's functionalities were removed and its exfiltration process was streamlined, which resulted in a leaner payload, around half its original size and a quicker infection process [11]. Some of the features removed included sandbox detection and evasion functionalities, the collection of desktop text files and screen captures, which were deemed unnecessary. At the same time, the code was improved in order to include new Chrome versions released after CryptBot’s first appearance in 2019. Finally, its exfiltration process was simplified: prior to its 2022 update, the malware saved stolen data in two separate folders before sending it to two separate command and control (C2) domains. Post update, the data is only saved in one location and sent to one C2 domain, which is hardcoded in the C2 transmission function of the code. This makes the infection process much more streamlined, taking only a few minutes from start to finish.
Aside from the update to its malware code, CryptBot regularly updates and refreshes its C2 domains and dropper websites, making it a highly fluctuating malware with constantly new indicators of compromise and distribution sites.
Even though CryptBot is less known than other info-stealers, it was reportedly infecting thousands of devices daily in the first months of 2020 [13] and its continued prevalence resulted in Google taking legal action against its distribution infrastructure at the end of April 2023 [14].
How is CryptBot obtained?
CryptBot is primarily distributed through malicious websites offering free and illegally modified software (i.e., cracked software) for common commercial programs (e.g., Microsoft Windows and Office, Adobe Photoshop, Google Chrome, Nitro PDF Pro) and video games. From these ‘malvertising’ pages, the user is redirected through multiple sites to the actual payload dropper page [15]. This distribution method has seen a gain in popularity amongst info-stealers in recent months and is also used by other malware families such as Raccoon Stealer and Vidar [16] [17].
A same network of cracked software websites can be used to download different malware strains, which can result in multiple simultaneous infections. Additionally, these networks often use search engine optimization (SEO) in order to make adverts for their malware distributing sites appear at the top of the Google search results page, thus increasing the chances of the malicious payloads being downloaded.
Furthermore, CryptBot leverages Pay-Per-Install (PPI) services such as 360Installer and PrivateLoader, a downloader malware family used to deliver payloads of multiple malware families operated by different threat actors [18] [19] [20]. The use of this distribution method for CryptBot payloads appears to have stemmed from its 2022 update. According to Google, 161 active domains were associated with 360Installer, of which 90 were associated with malware delivery activities and 29 with the delivery of CryptBot malware specifically. Google further identified hundreds of domains used by CryptBot as C2 sites, all of which appear to be hosted on the .top top-level domain [21].
This simple yet effective distribution tactic, combined with the MaaS model and the lucrative prospects of selling the stolen data resulted in numerous infections. Indeed, CryptBot was estimated to have infected over 670,000 computers in 2022 [14]. Even though the distribution method chosen means that most of the infected devices are likely to be personal computers, bring your own device (BYOD) policies and users’ tendency to reuse passwords means that corporate environments are also at risk.
CryptBot Attack Overview
In some cases observed by Darktrace, after connecting to malvertising websites, devices were seen making encrypted SSL connections to file hosting services such as MediaFire or Mega, while in others devices were observed connecting to an endpoint associated with a content delivery network. This is likely the location from where the malware payload was downloaded alongside cracked software, which is executed by the unsuspecting user. As the user expects to run an executable file to install their desired software, the malware installation often happens without the user noticing.
Some of the malvertising sites observed by Darktrace on customer deployments were crackful[.]com, modcrack[.]net, windows-7-activator[.]com and office-activator[.]com. However, in many cases detected by Darktrace, CryptBot was propagated via websites offering trojanized KMSPico software (e.g., official-kmspico[.]com, kmspicoofficial[.]com). KMSPico is a popular Microsoft Windows and Office product activator that emulates a Windows Key Management Services (KMS) server to activate licenses fraudulently.
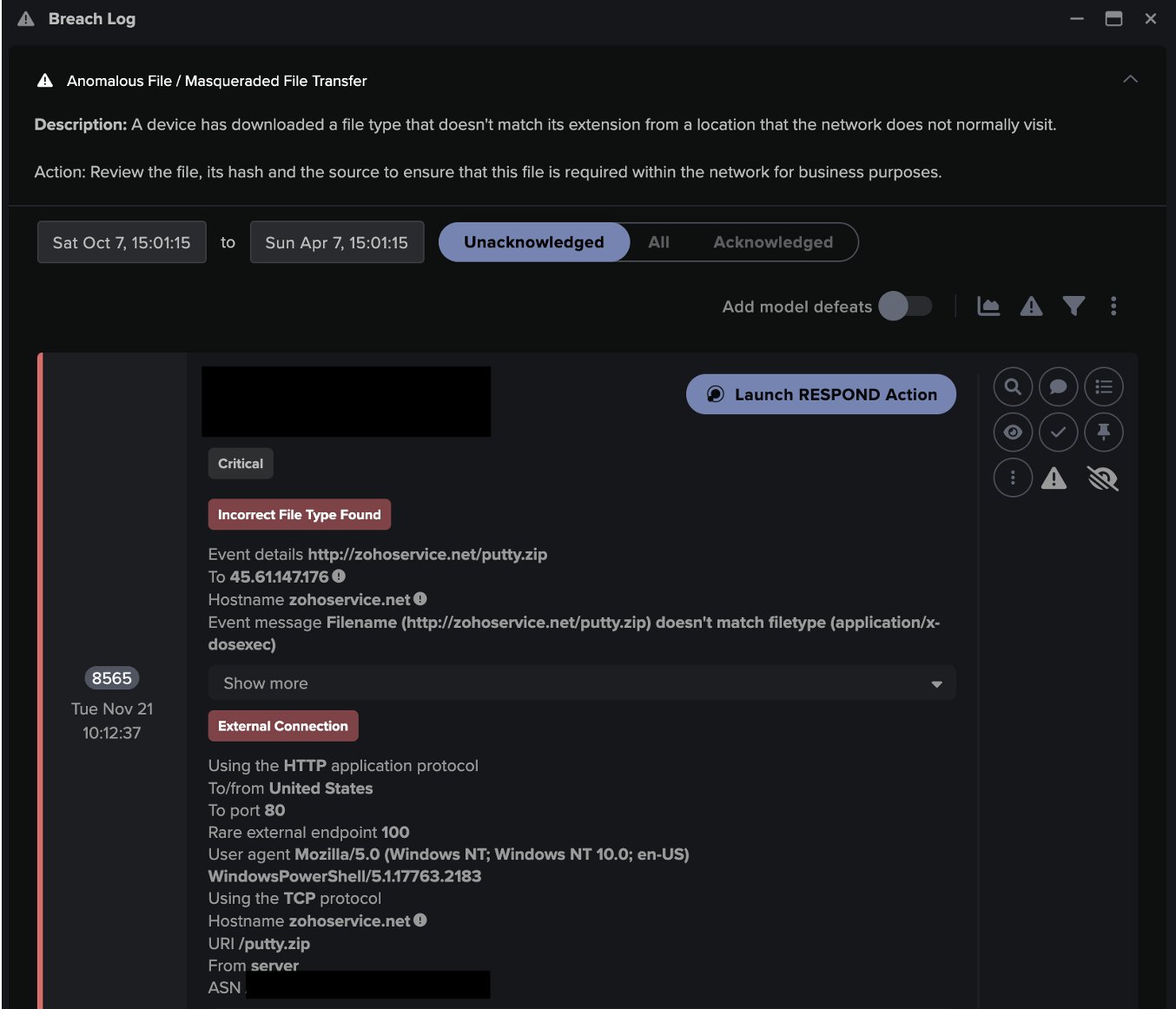
Once it has been downloaded and executed, CryptBot will search the system for confidential information and create a folder with a seemingly randomly generated name, matching the regex [a-zA-Z]{10}, to store the gathered sensitive data, ready for exfiltration.

This data is then sent to the C2 domain via HTTP POST requests on port 80 to the URI /gate.php. As previously stated, CryptBot C2 infrastructure is changed frequently and many of the domains seen by Darktrace had been registered within the previous 30 days. The domain names detected appeared to have been generated by an algorithm, following the regex patterns [a-z]{6}[0-9]{2,3}.top or [a-z]{6}[0-9]{2,3}.cfd. In several cases, the C2 domain had not been flagged as malicious by other security vendors or had just one detection. This is likely because of the frequent changes in the C2 infrastructure operated by the threat actors behind CryptBot, with new malicious domains being created periodically to avoid detection. This makes signature-based security solutions much less efficient to detect and block connections to malicious domains. Additionally, the fact that the stolen data is sent over regular HTTP POST requests, which are used daily as part of a multitude of legitimate processes such as file uploads or web form submissions, allows the exfiltration connections to blend in with normal and legitimate traffic making it difficult to isolate and detect as malicious activity.
In this context, anomaly-based security detections such as Darktrace DETECT are the best way to pick out these anomalous connections amidst legitimate Internet traffic. In the case of CryptBot, two DETECT models were seen consistently breaching for CryptBot-related activity: ‘Device / Suspicious Domain’, breaching for connections to 100% rare C2 .top domains, and ‘Anomalous Connection / POST to PHP on New External Host’, breaching on the data exfiltration HTTP POST request.
In deployments where Darktrace RESPOND was deployed, a RESPOND model breached within two seconds of the first HTTP POST request. If enabled in autonomous mode, RESPOND would block the data exfiltration connections, thus preventing the data safe from being sold in underground forums to other threat actors. In one of the cases investigated by Darktrace’s Threat Research team, DETECT was able to successfully identify and alert the customer about CryptBot-related malicious activity on a device that Darktrace had only begun to monitor one day before, showcasing how fast Darktrace’s Self-Learning AI learns every nuance of customer networks and the devices within it.
In most cases investigated by Darktrace, fewer than 5 minutes elapsed between the first connection to the endpoint offering free cracked software and the data being exfiltrated to the C2 domain. For example, in one of the attack chains observed in a university’s network, a device was seen connecting to the 100% rare endpoint official-kmspico[.]com at 16:53:47 (UTC).
![Device Event Log showing SSL connections to the official-kmspico[.]com malvertising website.](https://assets-global.website-files.com/626ff4d25aca2edf4325ff97/64948dd51ee68f78614ec851_blog%202.png)
One minute later, at 16:54:19 (UTC), the same device was seen connecting to two mega[.]co[.]nz subdomains and downloading around 13 MB of data from them. As mentioned previously, these connections likely represent the CryptBot payload and cracked software download.
![Device Event Log showing SSL connections to mega[.]com endpoints following the connection to the malvertising site.](https://assets-global.website-files.com/626ff4d25aca2edf4325ff97/64948e0b95ab2e7499b11e0c_blog%203.png)
At 16:56:01 (UTC), Darktrace detected the device making a first HTTP POST request to the 100% rare endpoint, avomyj24[.]top, which has been associated with CryptBot’s C2 infrastructure [22]. This initial HTTP POST connection likely represents the transfer of confidential data to the attacker’s infrastructure.

The full attack chain, from visiting the malvertising website to the malicious data egress, took less than three minutes to complete. In this circumstance, the machine-speed detection and response capabilities offered by Darktrace DETECT and RESPOND are paramount in order to stop CryptBot before it can successfully exfiltrates sensitive data. This is an incredibly quick infection timeline, with no lateral movement nor privilege escalation required to carry out the malware’s objective.

Darktrace Cyber AI Analyst incidents were also generated as a result of this activity, displaying all relevant information in one panel for easy review by customer security teams.

Conclusão
CryptBot info-stealer is fast, efficient, and apt at evading detection given its small size and swift process of data gathering and exfiltration via legitimate channels. Its constantly changing C2 infrastructure further makes it difficult for traditional security tools that really on rules and signatures or known indicators of compromise (IoCs) to detect these infections.
In the face of such a threat, Darktrace’s anomaly-based detection allows it to recognize subtle deviations in a device’s pattern of behavior that may signal an evolving threat and instantly bring it to the attention of security teams. Darktrace DETECT is able to distinguish between benign activity and malicious behavior, even from newly monitored devices, while Darktrace RESPOND can move at machine-speed to prevent even the fastest moving threat actors from stealing confidential company data, as it demonstrated here by stopping CryptBot infections in as little as 2 seconds.
Credit to Alexandra Sentenac, Cyber Analyst, Roberto Romeu, Senior SOC Analyst
Darktrace Model Detections
AI Analyst Coverage
- Possible HTTP Command and Control
DETECT Model Breaches
- Device / Suspicious Domain
- Anomalous Connection / POST to PHP on New External Host
- Anomalous Connection / Multiple HTTP POSTs to Rare Hostname
- Compromise / Multiple SSL to Rare DGA Domains
List of IOCs
MITRE ATT&CK Mapping
References
[1] https://www.malwarebytes.com/blog/threats/info-stealers
[2] https://cybelangel.com/what-are-infostealers/
[3] https://ke-la.com/information-stealers-a-new-landscape/
[4] https://darktrace.com/blog/vidar-info-stealer-malware-distributed-via-malvertising-on-google
[5] https://darktrace.com/blog/a-surge-of-vidar-network-based-details-of-a-prolific-info-stealer
[6] https://darktrace.com/blog/laplas-clipper-defending-against-crypto-currency-thieves-with-detect-respond
[7] https://darktrace.com/blog/amadey-info-stealer-exploiting-n-day-vulnerabilities
[8] https://cybelangel.com/what-are-infostealers/
[9] https://webz.io/dwp/the-top-10-dark-web-marketplaces-in-2022/
[10] https://www.accenture.com/us-en/blogs/security/information-stealer-malware-on-dark-web
[11] https://www.bleepingcomputer.com/news/security/revamped-cryptbot-malware-spread-by-pirated-software-sites/
[12] https://blogs.blackberry.com/en/2022/03/threat-thursday-cryptbot-infostealer
[13] https://www.deepinstinct.com/blog/cryptbot-how-free-becomes-a-high-price-to-pay
[14] https://blog.google/technology/safety-security/continuing-our-work-to-hold-cybercriminal-ecosystems-accountable/
[15] https://asec.ahnlab.com/en/31802/
[16] https://darktrace.com/blog/the-last-of-its-kind-analysis-of-a-raccoon-stealer-v1-infection-part-1
[17] https://www.trendmicro.com/pt_br/research/21/c/websites-hosting-cracks-spread-malware-adware.html
[18] https://intel471.com/blog/privateloader-malware
[19] https://cyware.com/news/watch-out-pay-per-install-privateloader-malware-distribution-service-is-flourishing-888273be
[20] https://regmedia.co.uk/2023/04/28/handout_google_cryptbot_complaint.pdf
[21] https://www.bankinfosecurity.com/google-wins-court-order-to-block-cryptbot-infrastructure-a-21905
[22] https://github.com/stamparm/maltrail/blob/master/trails/static/malware/cryptbot.txt

































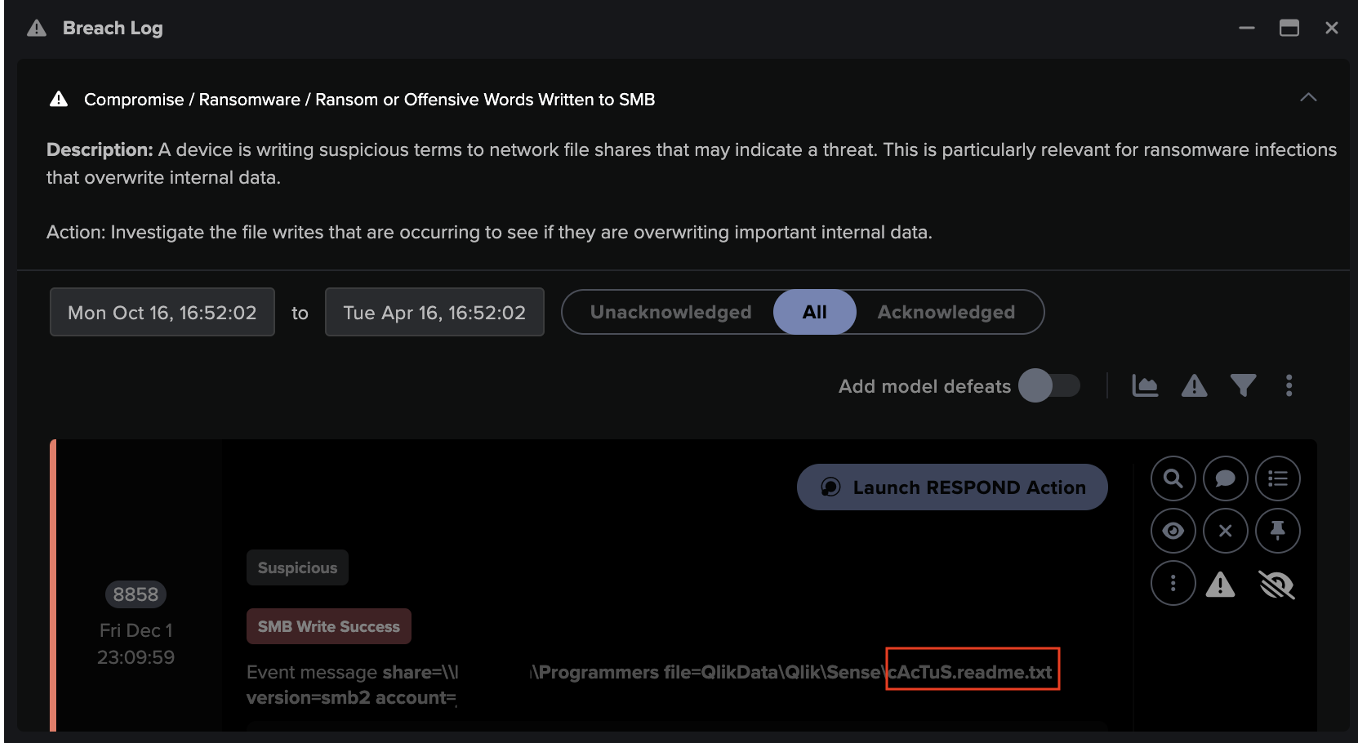
![Cyber AI Analyst Incident Log showing the offending device making over 1,000 connections to the suspicious hostname “zohoservice[.]net” over port 8383, within a specific period.](https://assets-global.website-files.com/626ff4d25aca2edf4325ff97/662971c1cf09890fd46729a1_Screenshot%202024-04-24%20at%201.55.10%20PM.png)